We’re entering a new era of optimizing for search engines. And no, SEO is not dead.
While many things stay the same in search, we can’t deny the new path we’re on with the introduction of machine-learning systems like Google’s RankBrain.
The concept of RankBrain may seem technical and daunting, but it’s one that CMOs — not just technically savvy SEOs — must understand to be competitive in the months to come.
In this post I cover:
What RankBrain is.
How search results are changing.
How to evolve your digital marketing strategy for machine learning search algorithms.
And why you might need PPC advertising even more than ever.
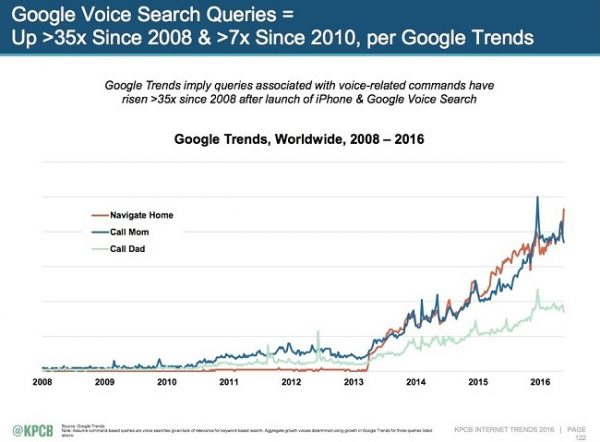
I believe that RankBrain is preparing for a world where voice search will become more and more the norm.
An Intro to RankBrain
RankBrain is a machine-learning artificial intelligence system that came onto the scene in 2015.
Bloomberg was the first among mainstream media to break the news of RankBrain, Google’s newest addition to search rankings.
And while we officially met RankBrain in 2015, Google was talking about it as early as 2013.
RankBrain is designed to better understand the meaning behind a searcher’s words. This 2013 post at Google discusses this concept of understanding word relationships if you want to learn more.
From the Bloomberg article we learned that 15 percent of queries per day have never been seen by Google before. RankBrain helps interpret those novel queries.
At the heart of RankBrain is a goal to better interpret search queries and serve the most relevant search results. This has been a lifelong goal of Google Search.
Read more: Bruce Clay
Also: How to Know If You’re at Risk When Google Switches to a Mobile-First Index (Flowchart)
While many things stay the same in search, we can’t deny the new path we’re on with the introduction of machine-learning systems like Google’s RankBrain.
The concept of RankBrain may seem technical and daunting, but it’s one that CMOs — not just technically savvy SEOs — must understand to be competitive in the months to come.
In this post I cover:
What RankBrain is.
How search results are changing.
How to evolve your digital marketing strategy for machine learning search algorithms.
And why you might need PPC advertising even more than ever.

I believe that RankBrain is preparing for a world where voice search will become more and more the norm.
An Intro to RankBrain
RankBrain is a machine-learning artificial intelligence system that came onto the scene in 2015.
Bloomberg was the first among mainstream media to break the news of RankBrain, Google’s newest addition to search rankings.
And while we officially met RankBrain in 2015, Google was talking about it as early as 2013.
RankBrain is designed to better understand the meaning behind a searcher’s words. This 2013 post at Google discusses this concept of understanding word relationships if you want to learn more.
From the Bloomberg article we learned that 15 percent of queries per day have never been seen by Google before. RankBrain helps interpret those novel queries.
At the heart of RankBrain is a goal to better interpret search queries and serve the most relevant search results. This has been a lifelong goal of Google Search.
Read more: Bruce Clay
Also: How to Know If You’re at Risk When Google Switches to a Mobile-First Index (Flowchart)
Last edited:






